Gut–brain axis
| Part of a series on |
| Microbiomes |
|---|
 |
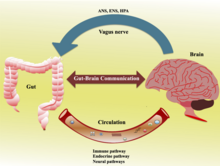
The gut–brain axis is the two-way biochemical signaling that takes place between the gastrointestinal tract (GI tract) and the central nervous system (CNS).[2] The term "gut–brain axis" is occasionally used to refer to the role of the gut microbiota in the interplay as well. The "microbiota–gut–brain (MGB or BGM) axis" explicitly includes the role of gut microbiota in the biochemical signaling events that take place between the GI tract and the CNS.[2][3][4] Broadly defined, the gut–brain axis includes the central nervous system, neuroendocrine system, neuroimmune systems, the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis (HPA axis), sympathetic and parasympathetic arms of the autonomic nervous system, the enteric nervous system, vagus nerve, and the gut microbiota.[2][4]
Chemicals released in the gut by the microbiome can vastly influence the development of the brain, starting from birth. A review from 2015 states that the microbiome influences the central nervous system by “regulating brain chemistry and influencing neuro-endocrine systems associated with stress response, anxiety and memory function”.[5] The gut, sometimes referred to as the “second brain”, functions off of the same type of neural network as the central nervous system, suggesting why it plays a significant role in brain function and mental health.[6]
The bidirectional communication is done by immune, endocrine, humoral and neural connections between the gastrointestinal tract and the central nervous system.[5] More research suggests that the gut microorganisms influence the function of the brain by releasing the following chemicals: cytokines, neurotransmitters, neuropeptides, chemokines, endocrine messengers and microbial metabolites such as "short-chain fatty acids, branched chain amino acids, and peptidoglycans”.[7] The intestinal microbiome can then divert these products to the brain via the blood, neuropod cells, nerves, endocrine cells and more to be determined.[8] The products then arrive at important locations in the brain, impacting different metabolic processes. Studies have confirmed communication between the hippocampus, the prefrontal cortex and the amygdala (responsible for emotions and motivation), which acts as a key node in the gut-brain behavioral axis.[9]
While IBS is the only disease confirmed to be directly influenced by the gut microbiome, many disorders (such as anxiety, autism, depression and schizophrenia) have been linked to the gut-brain axis as well.[7][10][8] The impact of the axis, and the various ways in which one can influence it, remains a promising research field which could result in future treatments for psychiatric, age-related, neurodegenerative and neurodevelopmental disorders. For example, according to a study[citation needed] from 2017, “probiotics have the ability to restore normal microbial balance, and therefore have a potential role in the treatment and prevention of anxiety and depression”.[11]
The first of the brain–gut interactions shown, was the cephalic phase of digestion, in the release of gastric and pancreatic secretions in response to sensory signals, such as the smell and sight of food. This was first demonstrated by Pavlov through Nobel prize winning research in 1904.[12][13]
Scientific interest in the field had already led to review in the second half of the 20th century. It was promoted further by a 2004 primary research study showing that germ-free (GF) mice showed an exaggerated HPA axis response to stress compared to non-GF laboratory mice.[2]
As of October 2016, most of the work done on the role of gut microbiota in the gut–brain axis had been conducted in animals, or on characterizing the various neuroactive compounds that gut microbiota can produce. Studies with humans – measuring variations in gut microbiota between people with various psychiatric and neurological conditions or when stressed, or measuring effects of various probiotics (dubbed "psychobiotics" in this context) – had generally been small and were just beginning to be generalized.[14] Whether changes to the gut microbiota are a result of disease, a cause of disease, or both in any number of possible feedback loops in the gut–brain axis, remained unclear.[15][2]
Enteric nervous system[edit]
The enteric nervous system is one of the main divisions of the nervous system and consists of a mesh-like system of neurons that governs the function of the gastrointestinal system; it has been described as a "second brain" for several reasons. The enteric nervous system can operate autonomously. It normally communicates with the central nervous system (CNS) through the parasympathetic (e.g., via the vagus nerve) and sympathetic (e.g., via the prevertebral ganglia) nervous systems. However, vertebrate studies show that when the vagus nerve is severed, the enteric nervous system continues to function.[16]
In vertebrates, the enteric nervous system includes efferent neurons, afferent neurons, and interneurons, all of which make the enteric nervous system capable of carrying reflexes in the absence of CNS input. The sensory neurons report on mechanical and chemical conditions. Through intestinal muscles, the motor neurons control peristalsis and churning of intestinal contents. Other neurons control the secretion of enzymes. The enteric nervous system also makes use of more than 30 neurotransmitters, most of which are identical to the ones found in CNS, such as acetylcholine, dopamine, and serotonin. More than 90% of the body's serotonin lies in the gut, as well as about 50% of the body's dopamine; the dual function of these neurotransmitters is an active part of gut–brain research.[17][18][19]
The first of the gut–brain interactions was shown to be between the sight and smell of food and the release of gastric secretions, known as the cephalic phase, or cephalic response of digestion.[12][13]
Gut–brain integration[edit]
The gut–brain axis, a bidirectional neurohumoral communication system, is important for maintaining homeostasis and is regulated through the central and enteric nervous systems and the neural, endocrine, immune, and metabolic pathways, and especially including the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis (HPA axis).[2] That term has been expanded to include the role of the gut microbiota as part of the "microbiome-gut-brain axis", a linkage of functions including the gut microbiota.[2][4][3]
Interest in the field was sparked by a 2004 study (Nobuyuki Sudo and Yoichi Chida) showing that germ-free mice (genetically homogeneous laboratory mice, birthed and raised in an antiseptic environment) showed an exaggerated HPA axis response to stress, compared to non-GF laboratory mice.[2]
The gut microbiota can produce a range of neuroactive molecules, such as acetylcholine, catecholamines, γ-aminobutyric acid, histamine, melatonin, and serotonin, which are essential for regulating peristalsis and sensation in the gut.[24] Changes in the composition of the gut microbiota due to diet, drugs, or disease correlate with changes in levels of circulating cytokines, some of which can affect brain function.[24] The gut microbiota also release molecules that can directly activate the vagus nerve, which transmits information about the state of the intestines to the brain.[24]
Likewise, chronic or acutely stressful situations activate the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis, causing changes in the gut microbiota and intestinal epithelium, and possibly having systemic effects.[24] Additionally, the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway, signaling through the vagus nerve, affects the gut epithelium and microbiota.[24] Hunger and satiety are integrated in the brain, and the presence or absence of food in the gut and types of food present also affect the composition and activity of gut microbiota.[24]
That said, most of the work that has been done on the role of gut microbiota in the gut–brain axis has been conducted in animals, including the highly artificial germ-free mice. As of 2016, studies with humans measuring changes to gut microbiota in response to stress, or measuring effects of various probiotics, have generally been small and cannot be generalized; whether changes to gut microbiota are a result of disease, a cause of disease, or both in any number of possible feedback loops in the gut–brain axis, remains unclear.[15]
The concept is of special interest in autoimmune diseases such as multiple sclerosis.[25] Nutrition and microbiota can influence both each other as well as the immune system, for example by modifying the Th17 and Treg cell frequencies and activity in animal models and preliminary trial in humans.[26][27]
The history of ideas about a relationship between the gut and the mind dates from the nineteenth century. [28] The concepts of dyspepsia and neurasthenia gastrica referred to the influence of the gut on human emotions and thoughts.[29][30]
Gut-brain-skin axis[edit]
A unifying theory that tied gastrointestinal mechanisms to anxiety, depression, and skin conditions such as acne was proposed as early as 1930.[31] In a paper in 1930, it was proposed that emotional states might alter normal intestinal microbiota which could lead to increased intestinal permeability and therefore contribute to systemic inflammation. Many aspects of this theory have been validated since then. Gut microbiota and oral probiotics have been found to influence systemic inflammation, oxidative stress, glycemic control, tissue lipid content, and mood.[32]
Gut microbiota[edit]
The gut microbiota is the complex community of microorganisms that live in the digestive tracts of humans and other animals. The gut metagenome is the aggregate of all the genomes of gut microbiota.[33] The gut is one niche that human microbiota inhabit.[34]
In humans, the gut microbiota has the largest quantity of bacteria and the greatest number of species, compared to other areas of the body.[35] In humans, the gut flora is established at one to two years after birth; by that time, the intestinal epithelium and the intestinal mucosal barrier that it secretes have co-developed in a way that is tolerant to, and even supportive of, the gut flora and that also provides a barrier to pathogenic organisms.[36][37]
The relationship between gut microbiota and humans is not merely commensal (a non-harmful coexistence), but rather a mutualistic relationship.[34] Human gut microorganisms benefit the host by collecting the energy from the fermentation of undigested carbohydrates and the subsequent absorption of short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), acetate, butyrate, and propionate.[35][38] Intestinal bacteria also play a role in synthesizing vitamin B and vitamin K as well as metabolizing bile acids, sterols, and xenobiotics.[34][38] The systemic importance of the SCFAs and other compounds they produce are like hormones and the gut flora itself appears to function like an endocrine organ;[38] dysregulation of the gut flora has been correlated with a host of inflammatory and autoimmune conditions.[35][39]
The composition of human gut microbiota changes over time, when the diet changes, and as overall health changes.[35][39] In general, the average human has over 1000 species of bacteria in their gut microbiome, with Bacteroidetes and Firmicutes being the dominant phyla. Diets higher in processed foods and unnatural chemicals can negatively alter the ratios of these species, while diets high in whole foods can positively alter the ratios. Additional health factors that may skew the composition of the gut microbiota are antibiotics and probiotics. Antibiotics have severe impacts on gut microbiota, ridding of both good and bad bacteria. Without proper rehabilitation, it can be easy for harmful bacteria to become dominant. Probiotics may help to mitigate this by supplying healthy bacteria into the gut and replenishing the richness and diversity of the gut microbiota. There are many strains of probiotics that can be administered depending on the needs of a specific individual.[40]
Bile acids and cognitive function[edit]
Microbial derived secondary bile acids produced in the gut may influence cognitive function.[41] Altered bile acid profiles occur in cases of mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's disease with an increase in cytotoxic secondary bile acids and a decrease in primary bile acids.[42] These findings suggest a role of the gut microbiome in the progression to Alzheimer's disease.[42] In contrast to the cytotoxic effect of secondary bile acids, the bile acid tauroursodeoxycholic acid may be beneficial in the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases.[43]
References[edit]
- ^ Chao, Yin-Xia; Gulam, Muhammad Yaaseen; Chia, Nicholas Shyh Jenn; Feng, Lei; Rotzschke, Olaf; Tan, Eng-King (2020). "Gut–Brain Axis: Potential Factors Involved in the Pathogenesis of Parkinson's Disease". Frontiers in Neurology. 11: 849. doi:10.3389/fneur.2020.00849. ISSN 1664-2295. PMC 7477379. PMID 32982910.
- ^ a b c d e f g h Sudo, N; Chida, Y; Aiba, Y (2004). "Postnatal microbial colonization programs the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal system for stress response in mice". J Physiol. 558 (1): 263–275. doi:10.1113/jphysiol.2004.063388. PMC 1664925. PMID 15133062. cited in: Wang, Y; Kasper, LH (May 2014). "The role of microbiome in central nervous system disorders". Brain Behav Immun. 38: 1–12. doi:10.1016/j.bbi.2013.12.015. PMC 4062078. PMID 24370461.
- ^ a b Mayer, EA; Knight, R; Mazmanian, SK; et al. (2014). "Gut microbes and the brain: paradigm shift in neuroscience". J Neurosci. 34 (46): 15490–15496. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3299-14.2014. PMC 4228144. PMID 25392516.
- ^ a b c Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. (2015). "The impact of gut microbiota on brain and behavior: implications for psychiatry". Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 18 (6): 552–558. doi:10.1097/MCO.0000000000000221. PMID 26372511. S2CID 21424690.
- ^ a b Carabotti, Marilia (2015). "The Gut-Brain Axis: Interactions between Enteric Microbiota, Central and Enteric Nervous Systems". Annals of Gastroenterology. 28 (2): 203–209. PMC 4367209. PMID 25830558.
- ^ "Gut-Brain Connection: What It is, Behavioral Treatments". Cleveland Clinic. Retrieved 2022-06-01.
- ^ a b Cryan, John F; O'Riordan, Kenneth J; Cowan, Caitlin; Kiran, Sandhu; Bastiaanssen, Thomaz; Boehme, Marcus (2019). "The Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis". Physiological Reviews. 99 (4): 1877–2013. doi:10.1152/physrev.00018.2018. PMID 31460832. S2CID 201661076.
- ^ a b Chen, Yijing; Xu, Jinying; Chen, Yu (13 June 2021). "Regulation of Neurotransmitters by the Gut Microbiota and Effects on Cognition in Neurological Disorders". Nutrients. 13 (6): 2099. doi:10.3390/nu13062099. PMC 8234057. PMID 34205336.
- ^ Cowan, Caitlin S M; Hoban, Alan E; Ventura-Silva, Ana Paula; Dinan, Timothy G; Clarke, Gerard; Cryan, John F (17 November 2017). "Gutsy Moves: The Amygdala as a Critical Node in Microbiota to Brain Signaling". BioEssays: News and Reviews in Molecular, Cellular and Developmental Biology. 40 (1). doi:10.1002/bies.201700172. PMID 29148060. S2CID 205478039.
- ^ Dolan, Eric W. (2023-05-19). "New study links disturbed energy metabolism in depressed individuals to disruption of the gut microbiome". PsyPost. Retrieved 2023-05-19.
- ^ Clapp, Megan; Aurora, Nadia; Herrera, Lindsey; Bhatia, Manisha; Wilen, Emily; Wakefield, Sarah (15 September 2017). "Gut Microbiota's Effect on Mental Health: The Gut-Brain Axis". Clinics and Practice. 7 (4): 987. doi:10.4081/cp.2017.987. PMC 5641835. PMID 29071061.
- ^ a b Filaretova, L; Bagaeva, T (2016). "The Realization of the Brain–Gut Interactions with Corticotropin-Releasing Factor and Glucocorticoids". Current Neuropharmacology. 14 (8): 876–881. doi:10.2174/1570159x14666160614094234. PMC 5333583. PMID 27306034.
- ^ a b Smeets, PA; Erkner, A; de Graaf, C (November 2010). "Cephalic phase responses and appetite". Nutrition Reviews. 68 (11): 643–55. doi:10.1111/j.1753-4887.2010.00334.x. PMID 20961295.
- ^ Wang, Huiying; Lee, In-Seon; Braun, Christoph; Enck, Paul (October 2016). "Effect of Probiotics on Central Nervous System Functions in Animals and Humans: A Systematic Review". J Neurogastroenterol Motil. 22 (4): 589–605. doi:10.5056/jnm16018. PMC 5056568. PMID 27413138.
- ^ a b Schneiderhan, J; Master-Hunter, T; Locke, A (2016). "Targeting gut flora to treat and prevent disease". J Fam Pract. 65 (1): 34–8. PMID 26845162. Archived from the original on 2016-08-15. Retrieved 2016-06-25.
- ^ Li, Ying; Owyang, Chung (September 2003). "Musings on the Wanderer: What's New in Our Understanding of Vago-Vagal Reflexes? V. Remodeling of vagus and enteric neural circuitry after vagal injury". American Journal of Physiology. Gastrointestinal and Liver Physiology. 285 (3): G461–9. doi:10.1152/ajpgi.00119.2003. PMID 12909562.
- ^ Pasricha, Pankaj Jay. "Stanford Hospital: Brain in the Gut – Your Health". YouTube.
- ^ Martinucci, I; et al. (2015). "Genetics and pharmacogenetics of aminergic transmitter pathways in functional gastrointestinal disorders". Pharmacogenomics. 16 (5): 523–39. doi:10.2217/pgs.15.12. hdl:11577/3166305. PMID 25916523.
- ^ Smitka, K; et al. (2013). "The role of "mixed" orexigenic and anorexigenic signals and autoantibodies reacting with appetite-regulating neuropeptides and peptides of the adipose tissue-gutbrain axis: relevance to food intake and nutritional status in patients with anorexia nervosa and bulimia nervosa". Int J Endocrinol. 2013: 483145. doi:10.1155/2013/483145. PMC 3782835. PMID 24106499.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i Zhang LS, Davies SS (April 2016). "Microbial metabolism of dietary components to bioactive metabolites: opportunities for new therapeutic interventions". Genome Med. 8 (1): 46. doi:10.1186/s13073-016-0296-x. PMC 4840492. PMID 27102537.
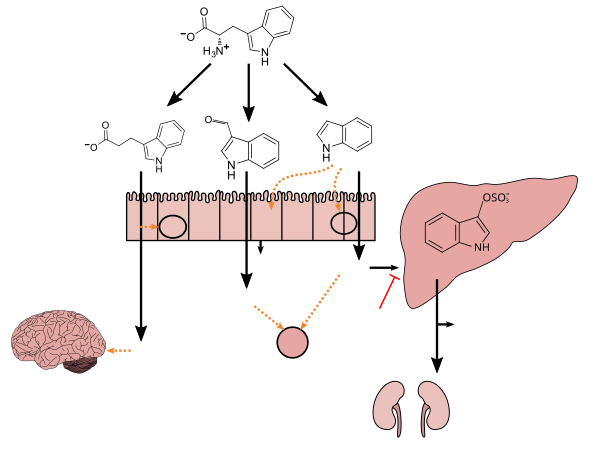
Lactobacillus spp. convert tryptophan to indole-3-aldehyde (I3A) through unidentified enzymes [125]. Clostridium sporogenes convert tryptophan to IPA [6], likely via a tryptophan deaminase. ... IPA also potently scavenges hydroxyl radicals
Table 2: Microbial metabolites: their synthesis, mechanisms of action, and effects on health and disease
Figure 1: Molecular mechanisms of action of indole and its metabolites on host physiology and disease - ^ Wikoff WR, Anfora AT, Liu J, Schultz PG, Lesley SA, Peters EC, Siuzdak G (March 2009). "Metabolomics analysis reveals large effects of gut microflora on mammalian blood metabolites". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 106 (10): 3698–3703. Bibcode:2009PNAS..106.3698W. doi:10.1073/pnas.0812874106. PMC 2656143. PMID 19234110.
Production of IPA was shown to be completely dependent on the presence of gut microflora and could be established by colonization with the bacterium Clostridium sporogenes.
IPA metabolism diagram - ^ "3-Indolepropionic acid". Human Metabolome Database. University of Alberta. Retrieved 12 June 2018.
- ^ Chyan YJ, Poeggeler B, Omar RA, Chain DG, Frangione B, Ghiso J, Pappolla MA (July 1999). "Potent neuroprotective properties against the Alzheimer beta-amyloid by an endogenous melatonin-related indole structure, indole-3-propionic acid". J. Biol. Chem. 274 (31): 21937–21942. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.31.21937. PMID 10419516. S2CID 6630247.
[Indole-3-propionic acid (IPA)] has previously been identified in the plasma and cerebrospinal fluid of humans, but its functions are not known. ... In kinetic competition experiments using free radical-trapping agents, the capacity of IPA to scavenge hydroxyl radicals exceeded that of melatonin, an indoleamine considered to be the most potent naturally occurring scavenger of free radicals. In contrast with other antioxidants, IPA was not converted to reactive intermediates with pro-oxidant activity.
- ^ a b c d e f Petra, AI; et al. (May 2015). "Gut-Microbiota-Brain Axis and Its Effect on Neuropsychiatric Disorders With Suspected Immune Dysregulation". Clin. Ther. 37 (5): 984–95. doi:10.1016/j.clinthera.2015.04.002. PMC 4458706. PMID 26046241.
- ^ Parodi, Benedetta; Kerlero de Rosbo, Nicole (2021-09-21). "The Gut-Brain Axis in Multiple Sclerosis. Is Its Dysfunction a Pathological Trigger or a Consequence of the Disease?". Frontiers in Immunology. 12: 718220. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2021.718220. ISSN 1664-3224. PMC 8490747. PMID 34621267.
- ^ Wilck, Nicola; Matus, Mariana G.; Kearney, Sean M.; Olesen, Scott W.; Forslund, Kristoffer; Bartolomaeus, Hendrik; Haase, Stefanie; Mähler, Anja; Balogh, András; Markó, Lajos; Vvedenskaya, Olga (November 2017). "Salt-responsive gut commensal modulates TH17 axis and disease". Nature. 551 (7682): 585–589. Bibcode:2017Natur.551..585W. doi:10.1038/nature24628. ISSN 1476-4687. PMC 6070150. PMID 29143823.
- ^ Duscha, Alexander; Gisevius, Barbara; Hirschberg, Sarah; Yissachar, Nissan; Stangl, Gabriele I.; Eilers, Eva; Bader, Verian; Haase, Stefanie; Kaisler, Johannes; David, Christina; Schneider, Ruth (2020-03-19). "Propionic Acid Shapes the Multiple Sclerosis Disease Course by an Immunomodulatory Mechanism". Cell. 180 (6): 1067–1080.e16. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.035. ISSN 1097-4172. PMID 32160527. S2CID 212643941.
- ^ Miller, Ian (2018-11-08). "The gut–brain axis: historical reflections". Microbial Ecology in Health and Disease. Informa UK Limited. 29 (2): 1542921. doi:10.1080/16512235.2018.1542921. ISSN 1651-2235. PMC 6225396. PMID 30425612.
- ^ Manon Mathias and Alison M. Moore (eds), Gut Feeling and Digestive Health in Nineteenth-Century Literature, History and Culture. New York: Palgrave, 2018. ISBN 9780230303454
- ^ Alison M. Moore, Manon Mathias and Jørgen Valeur, Microbial Ecology in Health and Disease, Volume 30 (1), Special issue on the Gut–Brain Axis in History and Culture, 2019
- ^ Stokes; Pillsbury (December 1930). "The effect on the skin of emotional and nervous states: Theoretical and practical consideration of a gastro-intestinal mechanism". Archives of Dermatology and Syphilology. 22 (6): 962–993. doi:10.1001/archderm.1930.01440180008002.
- ^ Bowe, W. P.; Logan, A. C. (2011). "Acne vulgaris, probiotics and the gut-brain-skin axis - back to the future?". Gut Pathogens. 3 (1): 1. doi:10.1186/1757-4749-3-1. PMC 3038963. PMID 21281494.
- ^ Saxena, R.; Sharma, V.K (2016). "A Metagenomic Insight Into the Human Microbiome: Its Implications in Health and Disease". In D. Kumar; S. Antonarakis (eds.). Medical and Health Genomics. Elsevier Science. p. 117. doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-420196-5.00009-5. ISBN 978-0-12-799922-7.
- ^ a b c Sherwood, Linda; Willey, Joanne; Woolverton, Christopher (2013). Prescott's Microbiology (9th ed.). New York: McGraw Hill. pp. 713–721. ISBN 978-0-07-340240-6. OCLC 886600661.
- ^ a b c d Quigley, EM (2013). "Gut bacteria in health and disease". Gastroenterol Hepatol (N Y). 9 (9): 560–9. PMC 3983973. PMID 24729765.
- ^ Sommer, F; Bäckhed, F (Apr 2013). "The gut microbiota--masters of host development and physiology". Nat Rev Microbiol. 11 (4): 227–38. doi:10.1038/nrmicro2974. PMID 23435359. S2CID 22798964.
- ^ Faderl, M; et al. (Apr 2015). "Keeping bugs in check: The mucus layer as a critical component in maintaining intestinal homeostasis". IUBMB Life. 67 (4): 275–85. doi:10.1002/iub.1374. PMID 25914114. S2CID 25878594.
- ^ a b c Clarke, G; et al. (Aug 2014). "Minireview: Gut microbiota: the neglected endocrine organ". Mol Endocrinol. 28 (8): 1221–38. doi:10.1210/me.2014-1108. PMC 5414803. PMID 24892638.
- ^ a b Shen, S; Wong, CH (Apr 2016). "Bugging inflammation: role of the gut microbiota". Clin Transl Immunol. 5 (4): e72. doi:10.1038/cti.2016.12. PMC 4855262. PMID 27195115.
- ^ Hemarajata, Peera; Versalovic, James (2013). "Effects of probiotics on gut microbiota: mechanisms of intestinal immunomodulation and neuromodulation". Therapeutic Advances in Gastroenterology. 6 (1): 39–51. doi:10.1177/1756283X12459294. ISSN 1756-2848. PMC 3539293. PMID 23320049.
- ^ Connell E, Le Gall G, Pontifex MG, Sami S, Cryan JF, Clarke G, Müller M, Vauzour D. Microbial-derived metabolites as a risk factor of age-related cognitive decline and dementia. Mol Neurodegener. 2022 Jun 17;17(1):43. doi: 10.1186/s13024-022-00548-6. PMID 35715821; PMCID: PMC9204954
- ^ a b MahmoudianDehkordi S, Arnold M, Nho K, Ahmad S, Jia W, Xie G, Louie G, Kueider-Paisley A, Moseley MA, Thompson JW, St John Williams L, Tenenbaum JD, Blach C, Baillie R, Han X, Bhattacharyya S, Toledo JB, Schafferer S, Klein S, Koal T, Risacher SL, Kling MA, Motsinger-Reif A, Rotroff DM, Jack J, Hankemeier T, Bennett DA, De Jager PL, Trojanowski JQ, Shaw LM, Weiner MW, Doraiswamy PM, van Duijn CM, Saykin AJ, Kastenmüller G, Kaddurah-Daouk R; Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative and the Alzheimer Disease Metabolomics Consortium. Altered bile acid profile associates with cognitive impairment in Alzheimer's disease-An emerging role for gut microbiome. Alzheimers Dement. 2019 Jan;15(1):76-92. doi: 10.1016/j.jalz.2018.07.217. Epub 2018 Oct 15. Erratum in: Alzheimers Dement. 2019 Apr;15(4):604. PMID 30337151; PMCID: PMC6487485
- ^ Khalaf K, Tornese P, Cocco A, Albanese A. Tauroursodeoxycholic acid: a potential therapeutic tool in neurodegenerative diseases. Transl Neurodegener. 2022 Jun 4;11(1):33. doi: 10.1186/s40035-022-00307-z. PMID 35659112; PMCID: PMC9166453
脳腸相関
脳腸相関(のうちょうそうかん、英: brain-gut interaction)とは、ヒトにおいて脳の状態が腸に影響を及ぼし、逆に腸の状態も脳に影響を及ぼす現象である。脳と腸は自律神経系やホルモン、サイトカインなどの液性因子を介して密に関連していることが知られている。この双方向的な関連を「脳腸相関」(英: brain-gut interaction)または「脳腸軸」(英: brain-gut axis)と呼ぶ[1]。これは成人だけではなく子供にも見られる[2]。
脳が腸へ与える影響[編集]
脳からは腸へ向けて神経が投射しており、精神的なストレスが消化管に影響を及ぼすことが知られている[3]。
腸が脳へ与える影響[編集]
様々な原因で腸の状態が悪いと、血液を介して脳が有害物質に曝される危険性が指摘されている。また腸内で腸内細菌叢が産生する物質が、脳に影響を与えることもある。
直感への影響[編集]
直感に頼ることが常に最適な意思決定戦略であるとは言えないが、実社会では時間的制約から直感に頼らざるを得ないことも少なくないため、脳の専門家は直感を完璧にするために脳腸相関を大切にすることを勧めている[4]。
脚注[編集]
- ^ 須藤信行. “脳腸相関(brain-gut interaction)”. 公益財団法人 腸内細菌学会. 用語集. (公財)腸内細菌学会事務局. 2020年6月3日閲覧。
- ^ 土生川千珠. “(2)過敏性腸症候群”. 一般社団法人 小児心身医学会. 小児の心身症-各論. 日本小児心身医学会事務局. 2022年5月7日閲覧。
- ^ “消化管研究班 脳腸相関”. 京都府立医科大学大学院医学研究科 消化器内科学教室. 消化器内科医局. 2020年6月3日時点のオリジナルよりアーカイブ。2020年6月3日閲覧。
- ^ “Trust Your Gut: How the Brain-Gut Connection Helps Us Decide Intuitively” (英語). www.brainfacts.org. 2023年6月9日閲覧。
参考文献[編集]
- 福土審「脳腸相関とストレス」『ストレス科学研究』第28巻、公益財団法人 パブリックヘルスリサーチセンター、2013年、16-19頁、doi:10.5058/stresskagakukenkyu.28.16、ISSN 1341-9986、NAID 130004726008。
- 福土審「ストレスと脳腸相関の法則を探る」『心身医学』第57巻第4号、2017年、335-342頁、doi:10.15064/jjpm.57.4_335。
- 須藤信行「脳機能と腸内細菌叢」『腸内細菌学雑誌』第31巻第1号、2017年、23-32頁、doi:10.11209/jim.31.23。
- 福土審「過敏性腸症候群と腸内細菌叢gut microbiota」『腸内細菌学雑誌』第32巻第1号、2018年、1-6頁、doi:10.11209/jim.32.1。
- 福土審「脳腸相関と機能性消化管障害」『日本消化器病学会雑誌』第117巻第10号、2020年、834-839頁、doi:10.11405/nisshoshi.117.834。
뇌장 상관
뇌장 상관은 인간 에서 뇌 상태가 장 에 영향 을 미치고 반대로 장 상태도 뇌 에 영향을 미치는 현상이다. 뇌와 장은 자율신경계 와 호르몬 , 사이토카인 등의 액성 인자를 통해 밀접하게 관련되어 있는 것으로 알려져 있다. 이 양방향 관계를 "뇌장 상관"( 영 : brain-gut interaction ) 또는 "뇌장 축"( 영 : brain-gut axis )이라고 부른다 [1] . 이것은 성인 뿐만 아니라 아이 에게도 보인다 [2] .
뇌가 장에 미치는 영향 [ 편집 ]
뇌에서는 장을 향해 신경이 투사 되고 있으며, 정신적인 스트레스가 소화관 에 영향을 미치는 것으로 알려져 있다 [3] .
장이 뇌에 미치는 영향 [ 편집 ]
다양한 원인으로 장의 상태가 나쁘면, 혈액을 통해 뇌가 유해물질 에 노출되는 위험성이 지적되고 있다. 또한 장내에서 장내 세균총이 생산하는 물질이 뇌에 영향을 줄 수 있다.
직감에 미치는 영향 [ 편집 ]
직감에 의지하는 것이 항상 최적의 의사결정 전략이라고는 말할 수 없지만, 실제 사회에서는 시간적 제약으로부터 직감에 의지하지 않을 수 없기 때문에 뇌 전문가는 직감을 완벽하게 하기 위해 뇌장 상관을 소중히하는 것이 좋습니다 [4] .
각주 [ 편집 ]
- ^ 스토 노부유키. “ 뇌장 상관(brain-gut interaction) ”. 공익 재단법인 장내 세균 학회 . 용어집 . (공재) 장내 세균 학회 사무국. 2020년 6월 3일 열람.
- ^ 도생천 치주. “ (2)과민성 장 증후군 ”. 일반 사단법인 소아 심신 의학회 . 소아의 심신증-각론 . 일본 소아 심신 의학회 사무국. 2022년 5월 7일 열람.
- ↑ “ 소화관 연구반 뇌장 상관 ”. 교토 부립 의과 대학 대학원 의학 연구과 소화기 내 과학 교실 . 소화기 내과 의국. 2020년 6월 3일 시점의 오리지널 보다 아카이브. 2020년 6월 3일에 확인함.
- ^ “ Trust Your Gut: How the Brain-Gut Connection Helps Us Decide Intuitively ” (영어). www.brainfacts.org . 2023년 6월 9일에 확인함.
참고 문헌 [ 편집 ]
- 복토심 「뇌장 상관과 스트레스 」 「스트레스 과학 연구」 제28권, 공익 재단법인 퍼블릭 헬스 리서치 센터, 2013년, 16-19쪽, doi : 10.5058 / stresskagakukenkyu.28.16 , ISSN 1301-097 .
- 복토심 「스트레스와 뇌장 상관의 법칙을 찾는다」 「심신 의학」 제57권 제4호, 2017년, 335-342쪽, doi : 10.15064/kr.57.4_335 .
- 스도 노부유키 「뇌 기능과 장내 세균총」 「장내 세균학 잡지」 제31권 제1호, 2017년, 23-32페이지, doi : 10.11209/jim.31.23 .
- 복토심 “ 과민성 장 증후군과 장내 세균총gut microbiota ” “장내 세균학 잡지” 제32권 제1호, 2018년, 1-6페이지, doi : 10.11209/jim.32.1 .
- 복토심 「뇌장 상관과 기능성 소화관 장애」 「일본 소화기 병학회 잡지」 제117권 제10호, 2020년, 834-839페이지, doi : 10.11405/nisshoshi.117.834 .