"Shahāb ad-Dīn" Yahya ibn Habash Suhrawardī (Persian: شهابالدین سهروردی, also known as Sohrevardi) (1154–1191) was a Persian[4][5][6][7][8][9][10][11] philosopher and founder of the Iranian school of Illuminationism, an important school in Islamic philosophy.
Shahāb ad-Dīn Yahya ibn Habash ibn Amirak as-Suhrawardī

Manuscript of Suhrawardi's Hikmat al-Ishraq. Copy created in post-Seljuq Iran, dated 13 October 1220
Personal
Born 1154
Sohrevard, Seljuk Empire
Died 1191 (aged 36–37)
Aleppo, Ayyubid Sultanate
Religion Islam,[1] Shafi Sunni[2]
School Perennial philosophy[3]
Other names Sohrevardi, Shahab al-Din
Senior posting
Based in Suhraward
Period in office 12th century
Contents
LifeEdit
Suhraward is a village located between the present-day towns of Zanjan and Bijar Garrus in Iran, where Suhrawardi was born in 1154.[10] He learned wisdom and jurisprudence in Maragheh (located today in the East Azerbaijan Province of Iran). His teacher was Majd al-Dīn Jīlī who was also Fakhr al-Din al-Razi’s teacher. He then went to Iraq and Syria for several years and developed his knowledge while he was there.
His life spanned a period of less than forty years during which he produced a series of works that established him as the founder of a new school of philosophy, called "Illuminism" (hikmat al-Ishraq). According to Henry Corbin, Suhrawardi "came later to be called the Master of Illumination (Shaikh-i-Ishraq) because his great aim was the renaissance of ancient Iranian wisdom".[15] which Corbin specifies in various ways as the "project of reviving the philosophy of ancient Persia".[16]
In 1186, at the age of thirty-two, he completed his magnum opus, The Philosophy of Illumination.
There are several contradictory reports of his death. The most commonly held view is that he was executed sometime between 1191 and 1208 in Aleppo on charges of cultivating Batini teachings and philosophy, by the order of al-Malik al-Zahir, son of Saladin.[12] Other traditions hold that he starved himself to death, others tell that he was suffocated or thrown from the wall of the fortress, then burned by some people.[17]
Teachings
Learn more
This section does not cite any sources. (January 2016)
Arising out of peripatetic philosophy as developed by Ibn Sina (Avicenna), Suhrawardi's illuminationist philosophy is critical of several of Ibn Sina's positions and radically departs from him in creating a symbolic language (mainly derived from ancient Iranian culture or Farhang-e Khosravani) to give expression to his wisdom (hikma).
Suhrawardi taught a complex and profound emanationist cosmology, in which all creation is a successive outflow from the original Supreme Light of Lights (Nur al-Anwar). The fundamental of his philosophy is pure immaterial light, where nothing is manifest, and which unfolds from the Light of Lights in a descending order of ever-diminishing intensity and, through complex interaction, gives rise to a "horizontal" array of lights, similar in conception to Platonic forms, that governs mundane reality. In other words, the universe and all levels of existence are but varying degrees of Light—light and darkness. In his division of bodies, he categorizes objects in terms of their reception or non-reception of light.
Suhrawardi considers a previous existence for every soul in the angelic realm before its descent to the realm of the body. The soul is divided into two parts, one remains in heaven and the other descends into the dungeon of the body. The human soul is always sad because it has been divorced from its other half. Therefore, it aspires to become reunited with it. The soul can only reach felicity again when it is united with its celestial part, which has remained in heaven. He holds that the soul should seek felicity by detaching itself from its tenebrous body and worldly matters and access the world of immaterial lights. The souls of the gnostics and saints, after leaving the body, ascend even above the angelic world to enjoy proximity to the Supreme Light, which is the only absolute Reality.
Suhrawardi elaborated the neoplatonic idea of an independent intermediary world, the imaginal world (ʿalam-i mithal عالم مثال). His views have exerted a powerful influence down to this day, particularly through Mulla Sadra’s combined peripatetic and illuminationist description of reality.
InfluenceEdit
Suhrawardi's Illuminationist project was to have far-reaching consequences for Islamic philosophy in Shi'ite Iran. His teachings had a strong influence on subsequent esoteric Iranian thought and the idea of “Decisive Necessity” is believed to be one of the most important innovations in the history of logical philosophical speculation, stressed by the majority of Muslim logicians and philosophers. In the 17th century, it was to initiate an Illuminationist Zoroastrian revival in the figure of the 16th century sage Azar Kayvan.
Suhrawardi and pre-Islamic Iranian thoughtEdit
Suhrawardi thought of himself as a reviver or resuscitator of the ancient Persian wisdom.[14] He states in Hikmat al-'Ishraq that:
There was among the ancient Persians a community of people guided by God who thus walked the true way, worthy Sage-Philosophers, with no resemblance to the Magi (Dualists). It is their precious philosophy of Light, the same as that to which the mystical experience of Plato and his predecessors bear witness, that we have revived in our book called Illuminationist Philosophy (Hikmat al-'Ishraq), and I have had no precursor in the way of such project.
Suhrawardi uses pre-Islamic Iranian gnosis, synthesizing it with Greek and Islamic wisdom. The main influence from pre-Islamic Iranian thought on Suhrawardi is in the realm of angelology and cosmology. He believed that the ancient Persians' wisdom was shared by Greek philosophers such as Plato as well as by the Egyptian Hermes and considered his philosophy of illumination a rediscovery of this ancient wisdom. According to Nasr, Suhrawardi provides an important link between the thought of pre-Islamic and post-Islamic Iran and a harmonious synthesis between the two. And Henry Corbin states: "In northwestern Iran, Sohravardi (d. 1191) carried out the great project of reviving the wisdom or theosophy of ancient pre-Islamic Zoroastrian Iran."[18]
In his work Alwah Imadi, Suhrawardi offers an esoteric interpretation of Ferdowsi's Epic of Kings (Shah Nama)[19] in which figures such as Fereydun, Zahak, Kay Khusraw[19] and Jamshid are seen as manifestations of the divine light. Seyyed Hossein Nasr states: "Alwah 'Imadi is one of the most brilliant works of Suhrawardi in which the tales of ancient Persia and the wisdom of gnosis of antiquity in the context of the esoteric meaning of the Quran have been synthesized".[19]
In this Persian work Partaw Nama and his main Arabic work Hikmat al-Ishraq, Suhrawardi makes extensive use of Zoroastrian symbolism[19] and his elaborate angelology is also based on Zoroastrian models.[19] The supreme light he calls both by its Quranic and Mazdean names, al-nur al-a'zam (the Supreme Light) and Vohuman (Bahman). Suhrawardi refers to the hukamayya-fars (Persian philosophers) as major practitioners of his Ishraqi wisdom and considers Zoroaster, Jamasp, Goshtasp, Kay Khusraw, Frashostar and Bozorgmehr as possessors of this ancient wisdom.
Among pre-Islamic Iranian symbols and concepts used by Suhrawardi are: minu (incorporeal world), giti (corporeal world), Surush (messenger, Gabriel), Farvardin (the lower world), gawhar (pure essence), Bahram, Hurakhsh (the Sun), shahriyar (archetype of species), isfahbad (light in the body), Amordad (Zoroastrian angel), Shahrivar (Zoroastrian angel), and the Kiyani Khvarenah.
With regards to the pre-Islamic Iranian concept of Khvarenah (glory), Suhrawardi mentions:[20]
"Whoever knows philosophy (hikmat) and perseveres in thanking and sanctifying the Light of the Lights, will be endowed with royal glory (kharreh) and with luminous splendor (farreh), and—as we have said elsewhere—divine light will further bestow upon him the cloak of royal power and value. Such a person shall then become the natural ruler of the universe. He shall be given aid from the high heavens, and whatever he commands shall be obeyed; and his dreams and inspirations will reach their uppermost, perfect pinnacle."
و هر که حکمت بداند و بر سپاس و تقدیس نور الانوار مداومت نماید، او را خرّه کیانی بدهند و فرّ نورانی ببخشند، و بارقی الاهی او را کسوت هیبت و بهاء بپوشاند و رئیس طبیعی شود عالم را، و او را از عالم اعلا نصرت رسد و سخن او در عالم علوی مسموع باشد، و خواب و الهام او به کمال رسد.»
Suhrawardi and Illumination schoolEdit
According to Hossein Nasr since Sheykh Ishraq was not translated into Western languages in the medieval period, Europeans had little knowledge about Suhrawardi and his philosophy. His school is ignored even now by later scholars.[21] Sheykh Ishraq tried to pose a new perspective on questions like the question of Existence. He not only caused peripatetic philosophers to confront new questions but also gave new life to the body of philosophy after Avicenna.[22]
According to John Walbridge, Suhrawardi's critique on peripatetic philosophy can be counted as an important turning point for his successors. Suhrawardi tried to criticize Avicennism in a new approach. Although Suhrawardi first was a pioneer of peripatetic philosophy, he later became a Platonist following a mystical experience. He is also considered as the one who revived the ancient wisdom of Persia by his philosophy of Illumination. His followers include other Persian philosophers such as Shahrazuri and Qutb al-Din al-Shirazi who tried to continue the way of their teacher. Suhrawardi made a distinction between two approaches in his Illuminationism: one approach is discursive and the other is intuitive.[23]
Scholarly views on SuhrawardiEdit
There are different and contradictory views regarding the character of Suhrawardi's school. Some scholars such as Hossein Ziai believe that the most important aspects of his thought are his logic and critique of the peripatetic conception of definitions.[19][page needed] On the other hand, scholars like Mehdi Hairi and Sayyid Jalal Addin Ashtiyyani, believe that Suhrawardi remained within the framework of peripatetic and neo-Avicennian philosophy. Mehdi Amin Razavi criticizes both these groups for ignoring the mystical dimension of Suhrawardi's writings.[19][page needed] In turn, scholars such as Henry Corbin and Hossein Nasr view Suhrawardi as a theosophist and focus on the mystical dimension of his work.[citation needed] Viewing in another way, Nadia Maftouni has analyzed Suhrawardi's works to figure out the elements of philosophy as a way of life. As she holds, the priority of practical reason to theoretical one, preferring intuitive knowledge over theoretical one, taking philosophy as a practice of attaining optional death, and proposing ways to heal mental diseases may well be considered the main elements of philosophy as a way of life in Suhrawardi's allegorical treatises.[24]
WritingsEdit
Suhrawardi left over 50 writings in Persian and Arabic.
Persian writingsEdit
- Partaw Nama ("Treatise on Illumination")
- Hayakal al-Nur al-Suhrawardi [Sohravardi, Shihaboddin Yahya] (1154–91) Hayakil al-nur ("The Temples of Light"), ed. M.A. Abu Rayyan, Cairo: al-Maktaba al-Tijariyyah al-Kubra, 1957. (The Persian version appears in oeuvres vol. III.)
- Alwah-i Imadi ("The tablets dedicated to Imad al-Din")
- Lughat-i Muran ("The language of Termites")
- Risalat al-Tayr ("The Treatise of the Bird")
- Safir-i Simurgh ("The Calling of the Simurgh")
- Ruzi ba Jama'at Sufiyaan ("A Day with the Community of Sufis")
- Fi Halat al-Tufulliyah ("On the State of Childhood")
- Awaz-i Par-i Jebrail ("The Chant of Gabriel's Wing")
- Aql-i Surkh ("The Red Intellect")
- Fi Haqiqat al-'Ishaq ("On the Reality of Love")
- Bustan al-Qolub ("The Garden of Hearts")
Arabic writings
- Kitab al-moqawamat
- Kitab al-mashari' wa'l-motarahat, Arabic texts edited with introduction in French by H. Corbin, Tehran: Imperial Iranian Academy of Philosophy, and Paris: Adrien Maisonneuve, 1976; vol II: I. Le Livre de la Théosophie oriental
- (Kitab Hikmat al-ishraq) 2. Le Symbole de foi des philosophes. 3. Le Récit de l'Exil occidental, Arabic texts edited with introduction in French by H. Corbin, Tehran: Imperial Iranian Academy of Philosophy, and Paris: Adrien Maisonneuve, 1977; vol III: oeuvres en persan, Persian texts edited with introduction in Persian by S.H. Nasr, introduction in French by H. Corbin, Tehran: Imperial Iranian Academy of Philosophy, and Paris: Adrien Maisonneuve, 1977. (Only the metaphysics of the three texts in Vol. I were published.) Vol. III contains a Persian version of the Hayakil al-nur, ed. and trans. H. Corbin
- L'Archange empourpré: quinze traités et récits mystiques, Paris: Fayard, 1976, contains translations of most of the texts in vol. III of oeuvres philosophiques et mystiques, plus four others. Corbin provides introductions to each treatise, and includes several extracts from commentaries on the texts. W.M. Thackston, Jr, The Mystical and Visionary Treatises of Shihabuddin Yahya Suhrawardi, London: Octagon Press, 1982, provides an English translation of most of the treatises in vol. III of oeuvres philosophiques et mystiques, which eschews all but the most basic annotation; it is therefore less useful than Corbin's translation from a philosophical point of view)
- Mantiq al-talwihat, ed. A.A. Fayyaz, Tehran: Tehran University Press, 1955. The logic of the Kitab al-talwihat (The Intimations)
- Kitab hikmat al-ishraq (The Philosophy of Illumination), trans H. Corbin, ed. and intro. C. Jambet, Le livre de la sagesse orientale: Kitab Hikmat al-Ishraq, Lagrasse: Verdier, 1986. (Corbin's translation of the Prologue and the Second Part (The Divine Lights), together with the introduction of Shams al-Din al-Shahrazuri and liberal extracts from the commentaries of Qutb al-Din al-Shirazi and Mulla Sadra. Published after Corbin's death, this copiously annotated translation gives to the reader without Arabic immediate access to al-Suhrawardi's illuminationist method and language)
English translationsEdit
- The Philosophy of Illumination: A New Critical Edition of the Text of Hikmat Al-Ishraq, edited by John Walbridge and Hossein Ziai, Provo, Brigham Young University Press, 1999.
- The Shape of Light: Hayakal al-Nur, interpreted by Shaykh Tosun Bayrak al-Jerrahi al-Halveti, Fons Vitae, 1998.
- The Mystical & Visionary Treatises of Suhrawardi, Translated by W.M. Thackson, Jr., London, The Octagon Press, 1982.
See alsoEditSuhrawardiyya
NotesEdit
- ^ Bosworth, C.E.; van Donzel, E.; Heinrichs, W.P.; Lecomte, G. (1997). Encyclopaedia of Islam. Vol. IX (San-Sze) (New ed.). Leiden, Netherlands: Brill. p. 781. ISBN 9004104224.
- ^ Marcotte, Roxanne (July 24, 2019). Zalta, Edward N. (ed.). The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy. Metaphysics Research Lab, Stanford University – via Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy.
- ^ "Suhrawardi considered himself to be the reviver of the perennial wisdom, philosophia perennis, or what he calls Hikmat al-khalidah or Hikmat al-atiqa which existed always among the Hindus, Persians, Babylonians, Egyptians, and the ancient Greeks up to the time of Plato." Paths and Havens, Hossein Nasr, p 128.
- ^ Ziai, H.(1997), “Al-Suhrawardi”, Encyclopaedia of Islam, New Ed., vol. 9: 782-784. Quote: "AL-SUHRAWARDI, SHIHAB AL-DIN YAHYA b. Habash b. Amirak, Abu'1-Futuh, well known Persian innovative philosopher-scientist, and founder of an independent, non-Aristotelian philosophical school named the "Philosophy of Illumination" (Ḥikmat al-ʿishraq)"
- ^ C. E. Butterworth, M. Mahdi, The Political Aspects of Islamic Philosophy, Harvard CMES Publishers, 406 pp., 1992, ISBN 0-932885-07-1 (see p.336)
- ^ John Walbridge, “The leaven of the ancients: Suhrawardī and the heritage of the Greeks”, State University of New York Press, 1999. Excerpt: “Suhrawardi, a 12th-century Persian philosopher, was a key figure in the transition of Islamic thought from the neo-Aristotelianism of Avicenna to the mystically oriented philosophy of later centuries.”
- ^ Seyyed Hossein Nasr, “The need for a sacred science”, SUNY Press, 1993. Pg 158: “Persian philosopher Suhrawardi refers in fact to this land as na-kuja abad, which in Persian means literally utopia, "no-place.”
- ^ Matthew Kapstein, University of Chicago Press, 2004, "The presence of light: divine radiance and religious experience", University of Chicago Press, 2004. pg 285: "the light of lights in the system of the Persian philosopher Suhrawardi"
- ^ Hossein Ziai. Illuminationism or Illuminationist philosophy, first introduced in the 12th century as a complete, reconstructed system distinct both from the Peripatetic philosophy of Avicenna and from theological philosophy. in: Encyclopædia Iranica, Volumes XII & XIII. 2004.
- ^ a b Edward Craig, Routledge Encyclopedia of Philosophy, "al-Suhrawardi, Shihab al-Din Yahya (1154-91)" Routledge 1998. Excerpt: "Shihab al-Din Yahya ibn Habash ibn Amirak Abu’l-Futuh al-Suhrawardi, known as al-Maqtul (the Slain One) in reference to his execution, and usually referred to as Shaykh al-Ishraq after his school of Illuminationist philosophy (hikmat al-ishraq), was born in AH 549/AD 1154 in the village of Suhraward in northwestern Iran."
- ^ Donald M. Borchert, Encyclopedia of Philosophy, Vol. 9 Gale / Cengage Learning 2nd. Edition, 2006. "suhraward ̄i, [addendum] (1155 or 1156–1191)" Excerpt: "Shihab al-Din Suhrawardi is one of the best known, innovative, yet controversial Persian philosophers in the history of philosophy in Iran."
- ^ a b Dabashi, Hamid (20 November 2012). The World of Persian Literary Humanism. Harvard University Press. p. 115. ISBN 978-0-674-06759-2.
- ^ The Cambridge History of Islam:, Volume 2 (1977) edited by P. M. Holt, Ann K. S. Lambton, Bernard Lewis pg 823: [1], p. 823, at Google Books
- ^ a b Henry Corbin, "The Voyage and the Messenger: Iran and Philosophy", North Atlantic Books, 1998. pg XLV: "There was among the ancient Persians a community of people guided by God who thus walked the true way, worthy Sage-Philosophers, with no resemblance to the Magi (Dualists). It is their precious philosophy of Light, the same as that to which the mystical experience of Plato and his predecessors bear witness, that we have revived in our book called Oriental Theosophy (Hikmat al-'Ishraq), and I have had no precursor in the way of such project."
- ^ H.Corbin, Spiritual Body and Celestial Earth (From Mazdean Iran to Shi'ite Iran), translated from French by Nancy Pearson, Princeton, 1977. (1:Paris, 1960), pg. 54.
- ^ Henry Corbin. The Voyage and the Messenger. Iran and Philosophy. Containing previous unpublished articles and lectures from 1948 to 1976. North Atlantic Books. Berkeley, California. 1998. ISBN 1-55643-269-0.
- ^ Muḥammad Kamāl, Mulla Sadra's transcendent philosophy, Ashgate Publishing, Ltd., 2006 (p.13)
- ^ Henry Corbin. The Man of Light in Iranian Sufism. Omega Publications, New York. 1994. ISBN 0-930872-48-7.
- ^ a b c d e f g Amin Razavi, M. (1997) Suhrawardi and the School of Illumination, Richmond: Curzon Press.
- ^ Hossein Ziai, "The book of radiance", Mazda Publisher, 1998. pg 84-85. Note that Ziai, whose extensive studies establish Suhrawardi as a rationalist thinker rather than an "Oriental mystic" translates the word Hikmat (wisdom) as "philosophy" rather than "wisdom," as is more common.
- ^ Hosein Nasr, Three Muslim Sages, 1997, p. 55.
- ^ Hosein Nasr, Islamic philosophy from its origin to the present, 2006, p. 86.
- ^ Walbridge, J., 'Suhrawardi and Illuminationism' in Adamson and Taylor, 2005, p. 201–223.
- ^ Maftouni, Nadia (2017). "فلسفه به مثابه مشی زندگی نزد شیخ اشراق" [Philosophy Taken as the Manner of Life by Shaikh al-ʿIshraq]. Research Quarterly in Islamic Ethics (in Persian). 10 (37): 17. Retrieved 16 September 2017.
ReferencesEdit
- Amin Razavi, M. (1997) Suhrawardi and the School of Illumination, Richmond: Curzon. (Clear and intelligent account of the main principles of his thought.)
- Corbin, H. (1971) En Islam iranien: aspects spirituels et philosophiques, vol. II: Sohrawardi et les Platoniciens de Perse, Paris: Gallimard. (Corbin devoted more of his time to the study of al-Suhrawardi than to any other figure, and this volume represents the essence of his research.)
- Jad Hatem Suhrawardî et Gibran, prophètes de la Terre astrale, Beyrouth, Albouraq, 2003
- Ha'iri Yazdi, M. (1992) The Principles of Epistemology in Islamic Philosophy: Knowledge by Presence, Albany, NY: State University of New York Press. (An original work on epistemology by a contemporary Iranian philosopher drawing critical comparisons between certain Islamic and Western philosophers; incorporates the best exposition in a Western language of al-Suhrawardi's theory of knowledge.)
- Nasr, S.H. (1983) Shihab al-Din Suhrawardi Maqtul, in M.M. Sharif (ed.) A History of Muslim Philosophy, vol. I, Wiesbaden: Otto Harrassowitz, 1963; repr. Karachi, no date. (Still one of the best short introductions to al-Suhrawardi, particularly useful on the cosmology.)
- al-Shahrazuri, Shams al-Din (c. 1288) Sharh hikmat al-ishraq (Commentary on the Philosophy of Illumination), ed. H. Ziai, Tehran: Institute for Cultural Studies and Research, 1993. (Critical edition of the 13th-century original; Arabic text only, but a useful short introduction in English.)
- Walbridge, John (1999) The Leaven of the Ancients: Suhrawardi and the Heritage of the Greeks, Albany, New York: State University of New York Press.
- Ziai, H. (1990) Knowledge and Illumination: a Study of Suhrawardi's Hikmat al-ishraq, Atlanta, GA: Scholars Press. (A pioneering study of al-Suhrawardi's logic and epistemology, particularly his criticism of the peripatetic theory of definition; unfortunately this work suffers from sloppy production.)
- Ziai, H. (1996a) Shihab al-Din Suhrawardi: Founder of the Illuminationist School, in S.H. Nasr and O. Leaman (eds) History of Islamic Philosophy, London: Routledge, 434-64. (Biography of al-Suhrawardi.)
- Ziai, H. (1996b) The Illuminationist Tradition, in S.H. Nasr and O. Leaman (eds) History of Islamic Philosophy, London: Routledge, 465-96. (General description of the Illuminationist tradition.)
External linksEditThe Shape of Light Translation of the Hayakal al-Nur, at archive.org.
Roxanne Marcotte. "Suhrawardi". In Zalta, Edward N. (ed.). Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy.
Biography at muslimphilosophy.com

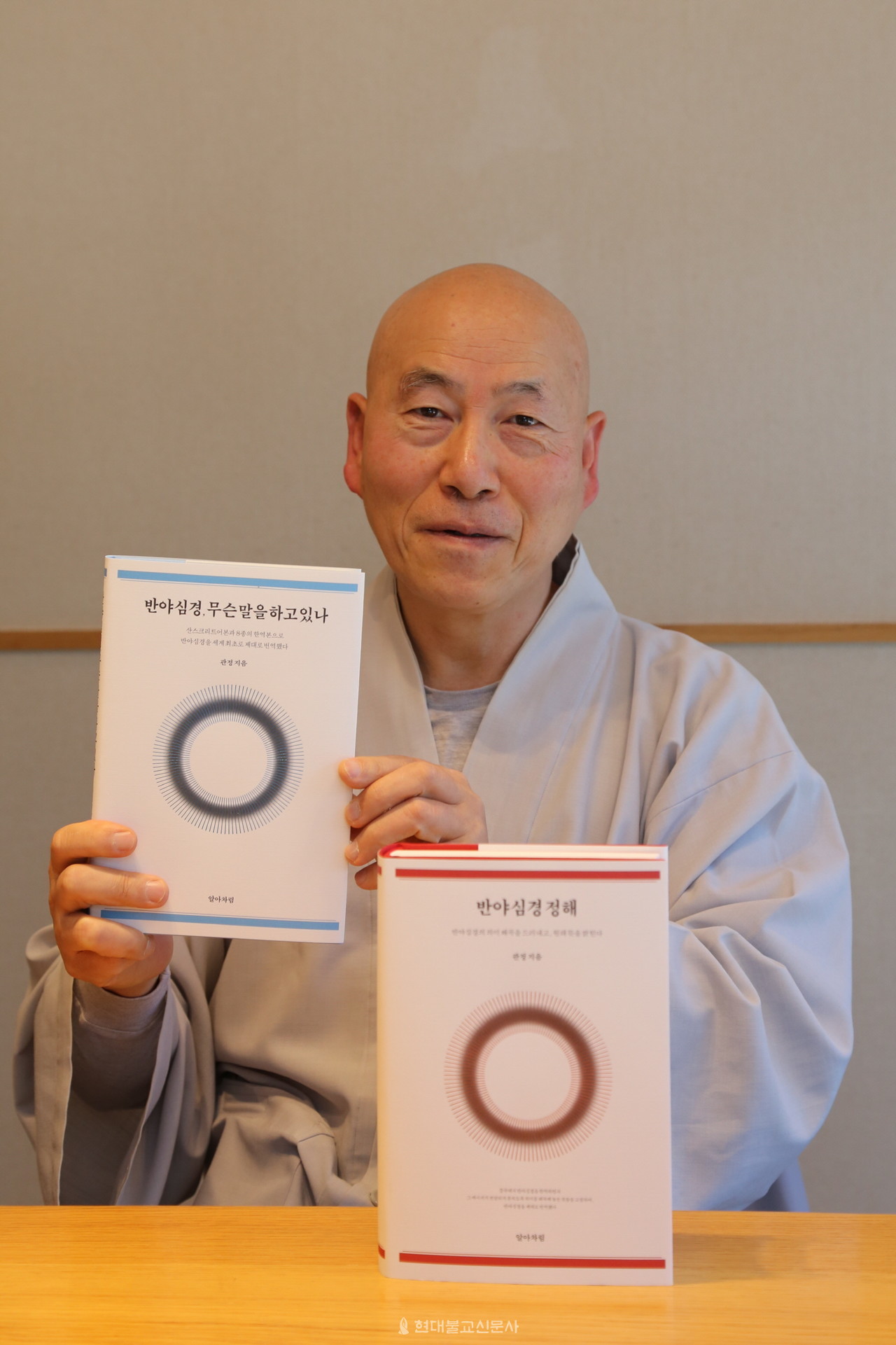
 반야심경 정해 / 관정 스님 지음/ 알아차림 펴냄 /65,000원
반야심경 정해 / 관정 스님 지음/ 알아차림 펴냄 /65,000원